Creep and Stress Rupture Testing
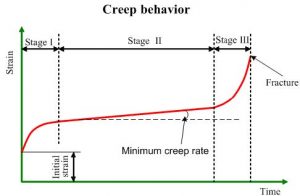
 Creep and stress rupture testing involves measuring deformation of materials at high temperatures under mechanical loads. The difference between creep and stress rupture depends on the applied load. Thus, if applied load is low compared to yield strength, the test is called creep test. Most materials when subjected to applied load will deform by several mechanisms. Metallic materials, ceramics, etc., in general deform by slip and twin along the crystallographic planes. But at high temperatures they may deform by grain boundary sliding or a combination of slip, twin and grain boundary sliding. Creep is generally associated with grain boundary sliding, while creep rupture is associated with slip and twin. Polymers and polymer composites deform by more complex mechanisms. The mechanism depends on the applied load, operating temperature and pressure etc. In general, when grain boundary sliding is a major deformation mode, the test is called creep test. Many applications such as gas turbine components, boilers, drill pipes used in oil and gas drilling, involve product and components operating at high temperatures. Thus, it is important to understand this deformation behavior of materials used to make components before components can be designed. Most materials will undergo some deformation at high temperatures even when the applied loads are very low compared to the yield strength of the materials.
Creep and stress rupture testing involves measuring deformation of materials at high temperatures under mechanical loads. The difference between creep and stress rupture depends on the applied load. Thus, if applied load is low compared to yield strength, the test is called creep test. Most materials when subjected to applied load will deform by several mechanisms. Metallic materials, ceramics, etc., in general deform by slip and twin along the crystallographic planes. But at high temperatures they may deform by grain boundary sliding or a combination of slip, twin and grain boundary sliding. Creep is generally associated with grain boundary sliding, while creep rupture is associated with slip and twin. Polymers and polymer composites deform by more complex mechanisms. The mechanism depends on the applied load, operating temperature and pressure etc. In general, when grain boundary sliding is a major deformation mode, the test is called creep test. Many applications such as gas turbine components, boilers, drill pipes used in oil and gas drilling, involve product and components operating at high temperatures. Thus, it is important to understand this deformation behavior of materials used to make components before components can be designed. Most materials will undergo some deformation at high temperatures even when the applied loads are very low compared to the yield strength of the materials.
Types of Creep Testing
Several different types of creep tests are available to assess high temperature deformation of materials. Typical examples are tensile creep, compressive creep, flexural creep, indentation creep, etc. Choice of tests depend on type of loading experienced in the applications, availability of materials for testing, test equipment, etc.
Capability – At TTL, we have conducted creep and stress rupture tests on ceramics, refractory alloys, polymer laminates and composites. We have capability to run tensile creep, flexural creep, compression creep tests at temperatures from room temperature up to 1000C in air and controlled atmosphere. When required we have the capability to design creep test frames for testing variety of materials under customized environments.
Some relevant standards:
- ASTM C1291 – Standard Test Method for Elevated Temperature Tensile Creep Strain, Creep Strain Rate, and Creep Time to Failure for Monolithic Advanced Ceramics
- ASTM C1337 – Standard Test Method for Creep and Creep Rupture of Continuous Fiber-Reinforced Advanced Ceramics Under Tensile Loading at Elevated Temperatures
- ASTM D2990 – Tensile, compressive, flexural creep and stress rupture of plastics
- ASTM E139 – Conducting creep, creep rupture, and stress rupture on metallic materials



Touchstone is committed to providing its customers with quality, reliable test results. That is why we have undertaken the rigorous steps needed to meet and secure the most stringent of test lab accreditations including ISO/IEC 17025, NADCAP 7101 (Materials Test Lab) and NADCAP 7122-I (Non-Metallics Materials Testing).
© 2024, Touchstone Testing Labs | Design by Wheelhouse Creative